In the volatile world of stock markets, investors often find themselves grappling with uncertainty and fear. One tool that has emerged as a crucial indicator of market sentiment is the US Stock Fear Index. This index, also known as the VIX, provides a snapshot of market anxiety, helping investors make informed decisions. In this article, we will delve into the details of the US Stock Fear Index, its significance, and how it can be used to gauge market sentiment.
What is the US Stock Fear Index?
The US Stock Fear Index, or the Volatility Index, is a measure of the market's expectation of 30-day forward volatility implied by S&P 500 index options. It is often referred to as the "fear gauge" because it reflects investors' fear and uncertainty about the future direction of the stock market. The VIX is calculated by taking the weighted average of implied volatilities for a range of S&P 500 index options.
How is the VIX Calculated?
The VIX is calculated using a complex formula that involves the prices of S&P 500 index options. The formula takes into account the strike price, time to expiration, and the risk-free interest rate. By analyzing the prices of these options, the VIX provides a measure of the market's expectation of volatility over the next 30 days.
Significance of the VIX
The VIX plays a crucial role in the financial markets for several reasons:
- Market Sentiment Indicator: The VIX is a powerful tool for gauging market sentiment. A high VIX indicates that investors are fearful of a market downturn, while a low VIX suggests optimism and confidence in the market.
- Risk Management: The VIX can be used by investors to manage their risk exposure. For example, when the VIX is high, investors may choose to hedge their portfolios using options strategies.
- Investment Opportunities: The VIX can also provide investment opportunities. For instance, inverse VIX ETFs can be used to profit from a rising VIX.
Case Study: The 2008 Financial Crisis
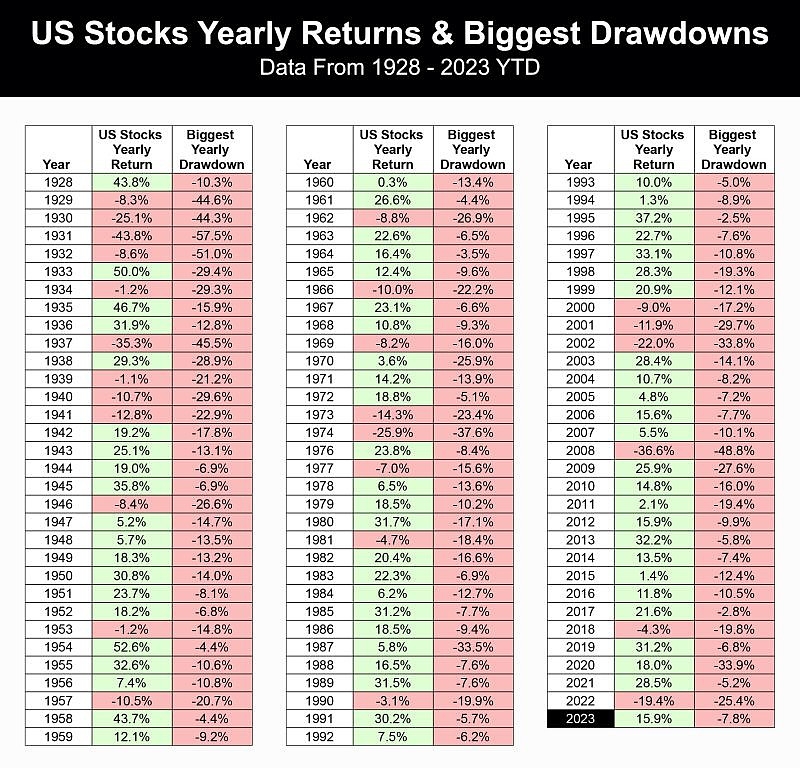
One of the most significant periods in the history of the VIX was during the 2008 financial crisis. As the crisis unfolded, the VIX skyrocketed, reaching an all-time high of 89.53 on October 24, 2008. This surge in the VIX reflected the extreme fear and uncertainty among investors during that period.
Conclusion
The US Stock Fear Index, or VIX, is a vital tool for understanding market sentiment and managing risk. By analyzing the VIX, investors can gain valuable insights into the market's expectations and make informed decisions. As the stock market continues to evolve, the VIX will remain a crucial indicator for investors and market participants alike.