In the vast and dynamic world of the US stock market, understanding who owns what can provide valuable insights into the market's structure and potential shifts. This article delves into the breakdown of who owns the US stock market, highlighting the key players and their influence.
1. Individual Investors
Individual investors form the largest segment of the US stock market. These investors include retail traders, pensioners, and those with personal savings. With the advent of online brokerage platforms, it has become easier for individuals to buy and sell stocks. Individual investors are known for their diverse investment strategies, ranging from short-term trading to long-term buy-and-hold approaches.
2. Mutual Funds and ETFs
Mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are popular among individual investors. These funds pool money from numerous investors to buy a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other assets. Mutual funds are actively managed, while ETFs are passively managed and often track a specific index. Both types of funds are significant players in the US stock market, with trillions of dollars in assets under management.
3. Retirement Plans
Retirement plans, such as 401(k)s and IRAs, are crucial components of the US stock market. Employers offer these plans to their employees, allowing them to save for retirement through tax-deferred contributions. Retirement plans often invest in a mix of stocks, bonds, and other assets, aiming to provide a secure retirement income. These plans are a significant source of long-term capital for the stock market.
4. Institutional Investors
Institutional investors, including pension funds, insurance companies, and endowments, play a vital role in the US stock market. These investors have substantial resources and often focus on long-term investment strategies. Pension funds, for instance, invest in a diverse range of assets to ensure a steady income for retirees. Insurance companies use their investments to support their insurance obligations. Endowments from universities and non-profit organizations often invest in stocks and bonds to generate income for their operations.
5. Foreign Investors
Foreign investors also have a significant presence in the US stock market. They include sovereign wealth funds, pension funds, and individual investors from other countries. These investors are attracted to the stability and growth potential of the US stock market. Foreign investors can influence market trends and valuation levels, making them a crucial component of the market's ecosystem.
Case Study: Technology Stocks
A prime example of the influence of different investors on the US stock market is the technology sector. Over the past few decades, technology stocks have experienced significant growth, driven by innovative companies like Apple, Microsoft, and Google. Individual investors have been instrumental in the rise of these stocks, often participating in initial public offerings (IPOs) and engaging in active trading. Institutional investors, including mutual funds and pension funds, have also played a significant role by investing in these companies for their long-term growth potential.
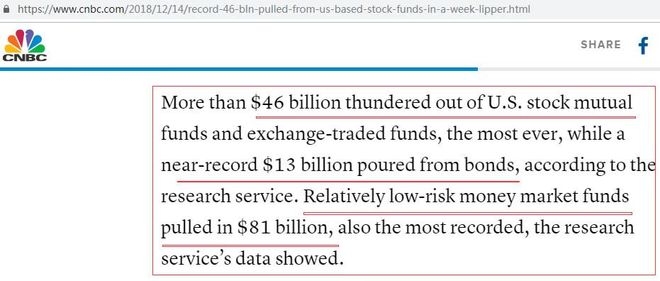
In conclusion, the US stock market is owned by a diverse group of investors, each with its own investment strategies and objectives. Understanding this breakdown can provide valuable insights into the market's structure and potential shifts. As the market continues to evolve, it is crucial to monitor the influence of different investor groups and their impact on market trends.